Too-Many-Cooks
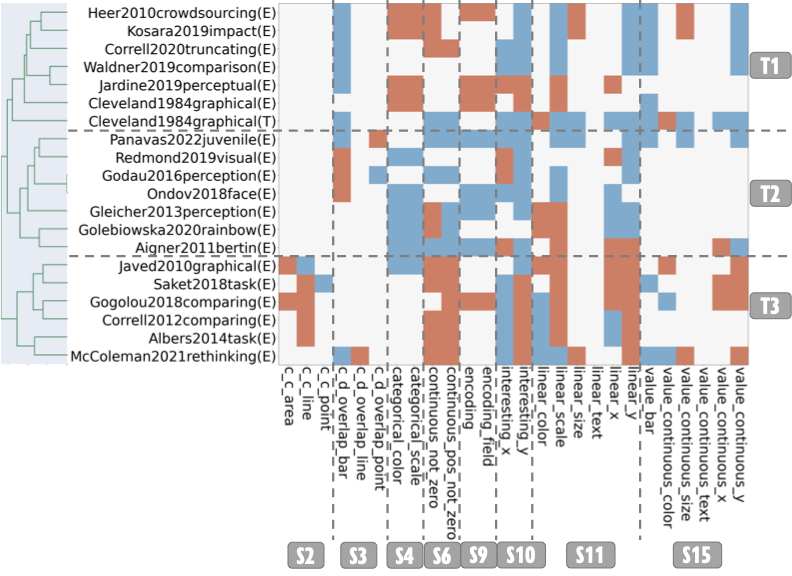
Findings from graphical perception can guide visualization recommendation algorithms in identifying effective visualization designs. However, existing algorithms use knowledge from, at best, a few studies, limiting our understanding of how complementary (or contradictory) graphical perception results influence generated recommendations. In this paper, we model graphical perception results from 30 papers in Draco—a framework to model visualization knowledge—to inform future recommendation algorithms. We investigate (1) how existing graphical perception literature covers the visualization design space and (2) how each study alters Draco’s behaviors, specifically how both soft constraint weights and resulting recommendations shift. By clustering studies that induce similar shifts in behavior, our findings quantify different “schools of thought” in graphical perception. Further, we identify conditions under which certain studies can dominate Draco’s recommendations, whereas others may have little influence. Given our findings, we discuss the potential for mutually reinforcing advancements in graphical perception and visualization recommendation research.