 ,
, Click for an MPEG movie (184K) of this interpolation.
Image morphing techniques can generate compelling 2D transitions between images. However, differences in object pose or viewpoint often cause unnatural distortions in image morphs that are difficult to correct manually. Using basic principles of projective geometry, this paper introduces a simple extension to image morphing that correctly handles 3D projective camera and scene transformations. The technique, called {\em view morphing}, works by prewarping two images prior to computing a morph and then postwarping the interpolated images. Because no knowledge of 3D shape is required, the technique may be applied to photographs and drawings, as well as rendered scenes. The ability to synthesize changes both in viewpoint and image structure affords a wide variety of interesting 3D effects via simple image transformations.
 , , |
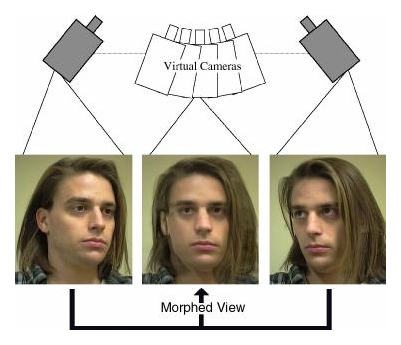
| View morphing between two images of an object taken from two
different viewpoints produces the illusion of physically moving a virtual
camera. Click for an MPEG movie (184K) of this interpolation. |
 |
| Morph between views of different faces produces simultaneous
interpolation of facial shape, color, and pose. Click for an MPEG movie (143K) of this interpolation. |
The examples on this page were generated using an interactive method to specify a sparse feature correspondence between each pair of images. We also explored the use of stereo matching algorithms to generate the correspondence information. For more information on this topic and discussion of the orthographic case, click here .
Two resolutions of Mona Lisa <--> Mona Lisa reflection:
| |
| Click for MPEG movie (84K) of Jude Shavlik <--> Chuck Dyer | |
| Click for view interpolations computed automatically from stereo correspondence. |
 |
 |
 Return to Steve Seitz's home page
Return to Steve Seitz's home page